Problem Definition:
Spam email is unwanted email that is sent to email users usually for commercial or malicious reasons. It is usually sent out in bulk. Browsing through such emails in a user’s inbox to look for genuine email is a waste of time. According to recent statistics, more than 40 percent of the emails sent out are spam. Therefore spam emails cause unnecessary wastage of storage space, internet bandwidth and computing resources. The spam emails can have varying degrees of affect on the users from annoyance to financial loss. To handle the threat of spam, email providers use spam filtering systems. Earlier ways to deal with spam included blacklisting and blocking known spam addresses.These days most spam filters use machine learning algorithms to stop the spam from hitting the inbox with a high accuracy.
Problem Statement:
Build a machine learning model to predict whether an email message is spam or not.
Dataset:
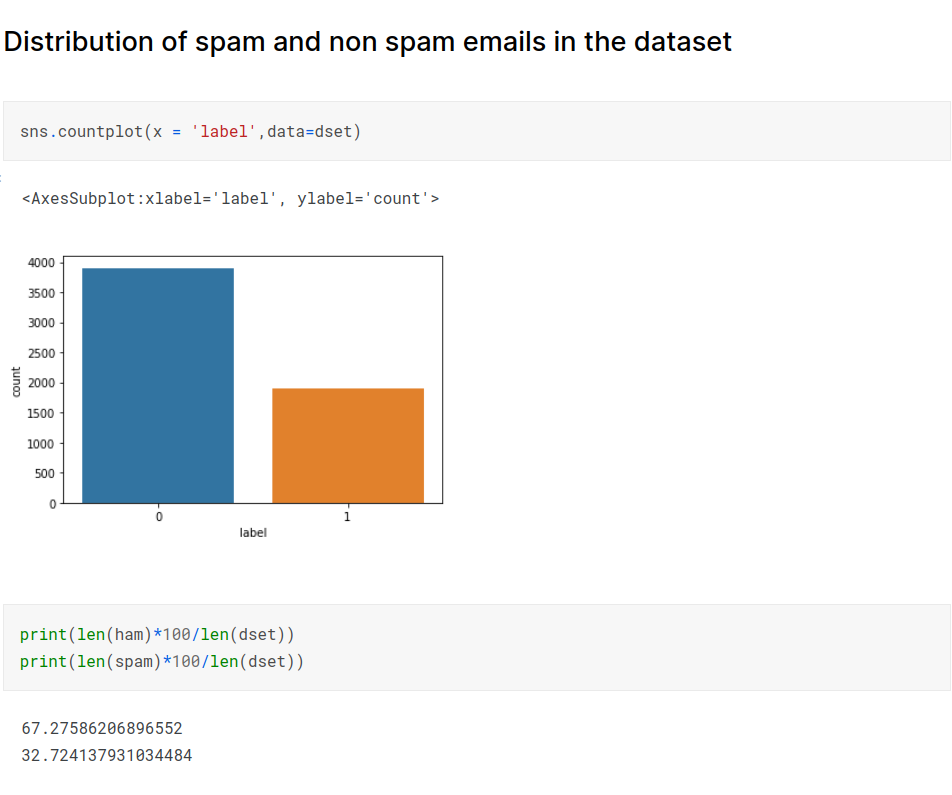
The dataset for the project was obtained from easy_ham, easy_ham_2, spam and spam_2 directories of the apache foundation’s spamassassin public corpus. https://spamassassin.apache.org/old/publiccorpus/. The dataset contains more than 5000 emails. The data was processed using numpy and pandas and put into a csv format with two columns email and label. The label contains two values. 1 represents spam and 0 represents not spam. The text column contains the email header (comprising From and Subject) and body of the email. Some emails contain html. The emails will need to be parsed to handle headers and encoding. In addition to the primary source, more data can be acquired from publicly available datasets if required.
Key Metric(KPI):
Accuracy
It is the percentage of correctly classified emails. Accuracy = Number of correctly classified emails / Total number of emails. Accuracy is used because correctly classifying spam and non spam emails is very important. ie True Positives and True negatives are very important.
Importing Libraries:
Exploratory Data Analysis:
Using python’s email module parse the emails
Using regular expressions and beautifulsoup to remove unwanted characters digits and converting text to lower case.
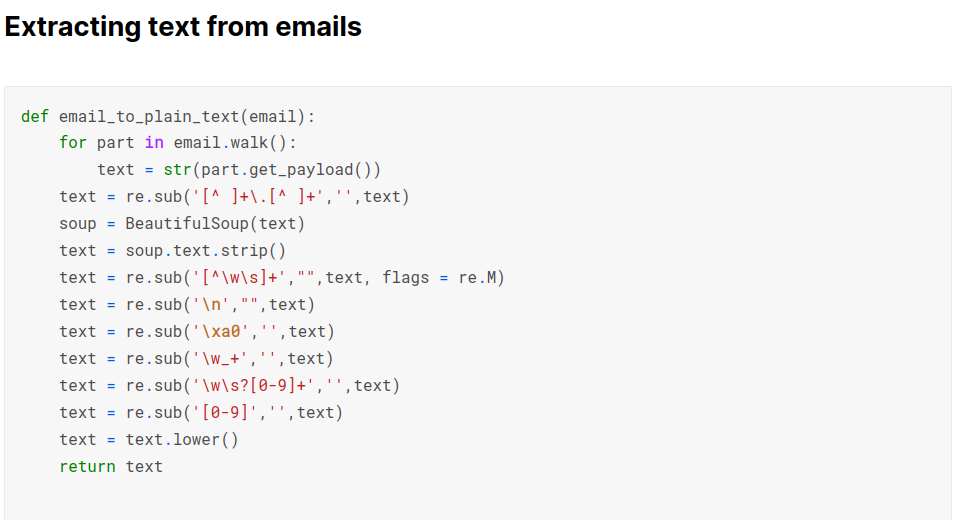
Using nlp techniques like stemming, lemmetization and tokenization on the text data
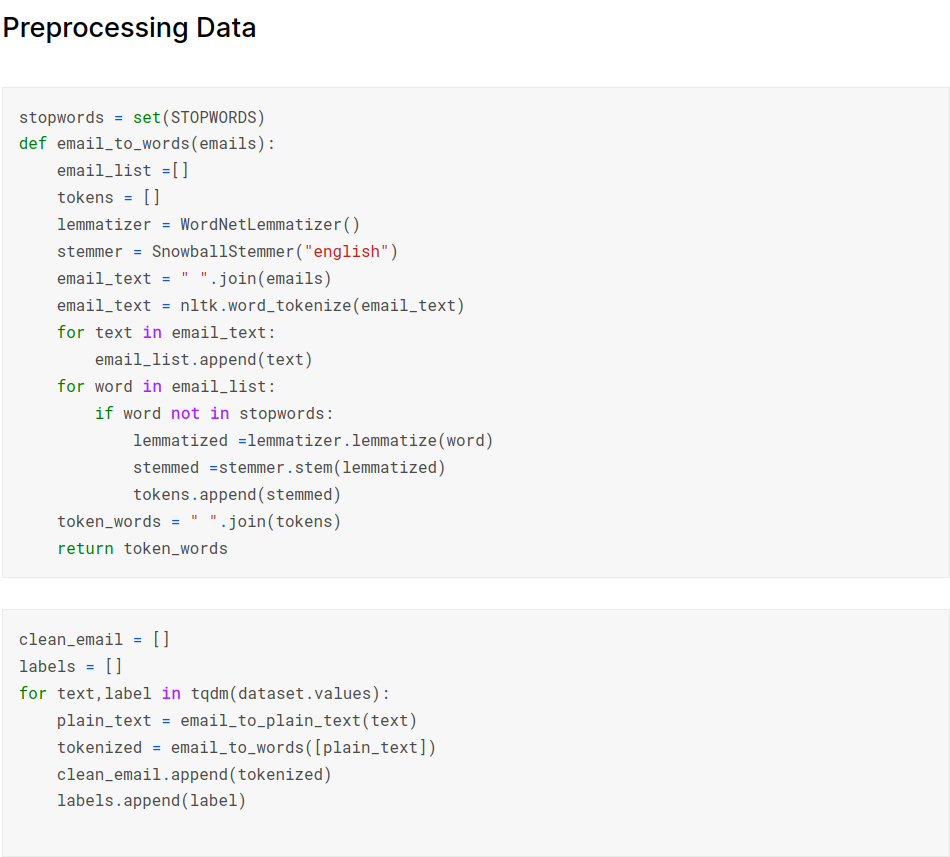
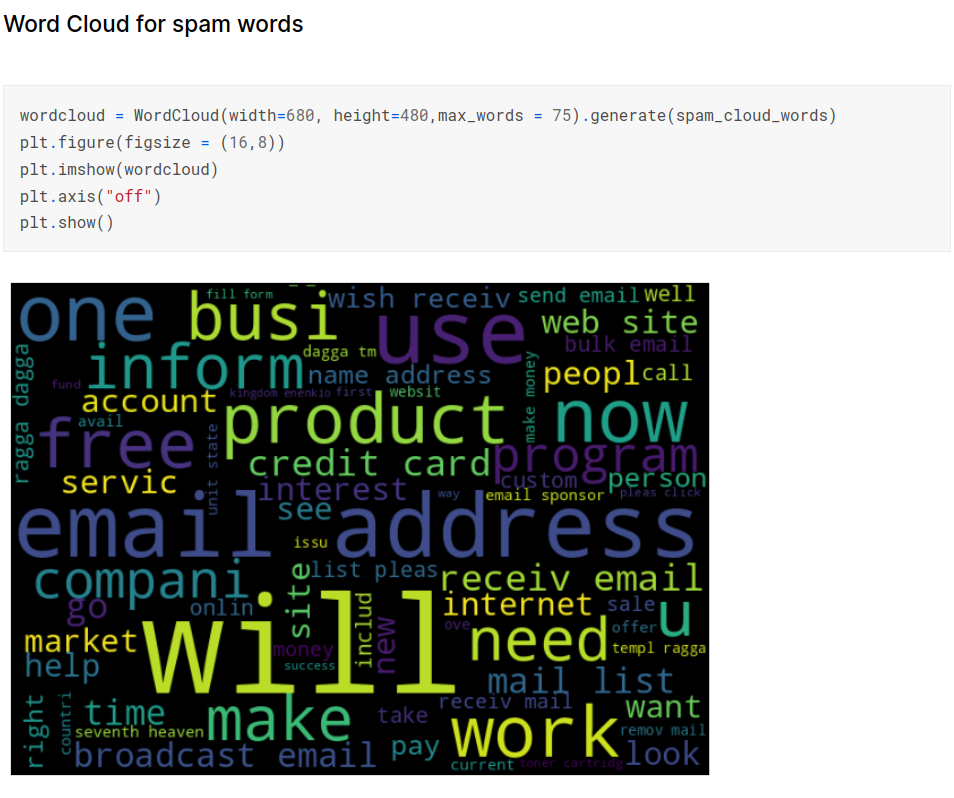
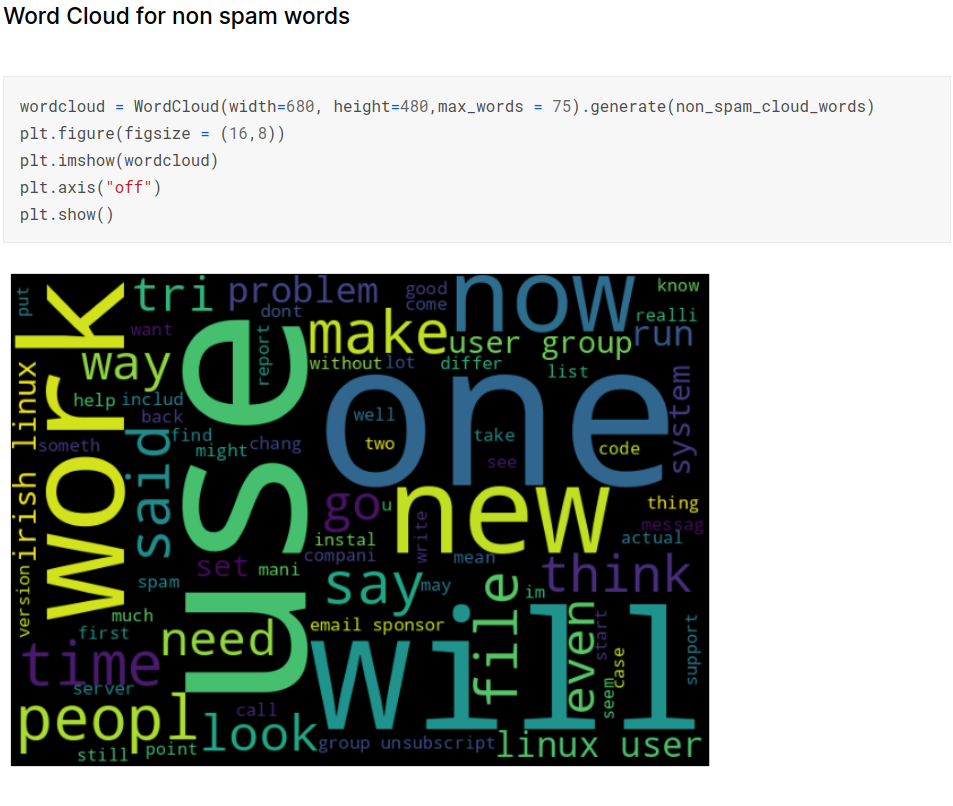
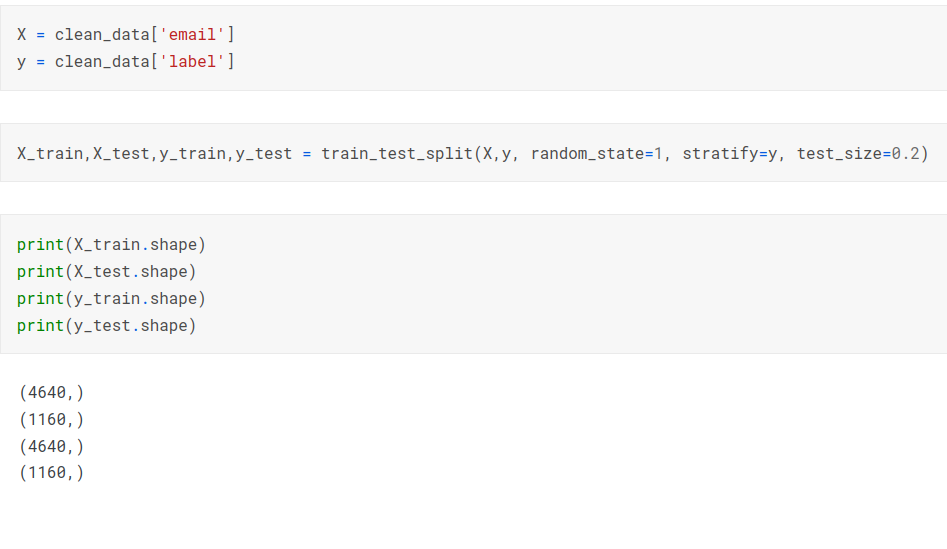
Splitting data into train and test sets:
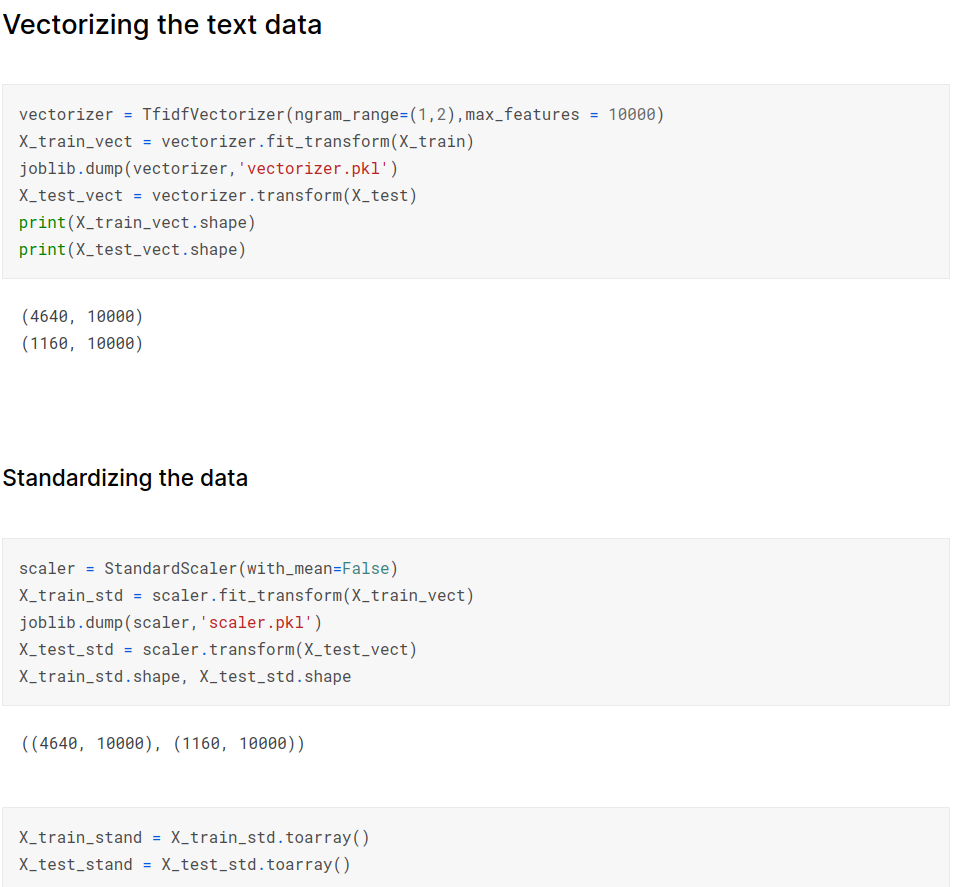
Using tfidf vectorizer to convert text data into vector representation
Modeling and Error Analysis:
Base-line model and metrics:
Logistic Regression:
Logistic regression is a simple linear classification model that can be applied for text classification. It uses sigmoid function or the logistic function for mapping predicted values to probabilities.

where z is the dot product of a data point with a weight vector + bias The loss function used for training the model is log loss.
Log loss is calculated as (− 1/𝑙𝑒𝑛(𝑦)) * 𝑠𝑢𝑚(𝑦 * 𝑙𝑜𝑔10(𝑦 𝑝 ) + (1 − 𝑦) * 𝑙𝑜𝑔10(1 − 𝑦 𝑝 ))
Weights and biases are updated using an optimizer like stochastic gradient descent to get the optimal values. The optimal weight and bias values are then passed to the sigmoid function to get probability values. If the probability value is greater than 0.5, then that is labeled as one class if it is less than 0.5 then it is labeled as the other class.
Logistic Regression Implementation
Initializing weights and bias

Sigmoid function

Loss function

Gradient with respect to weights

Gradient with respect to bias

Finding optimal values for weights and bias terms on the training data using SGD

Predicting labels

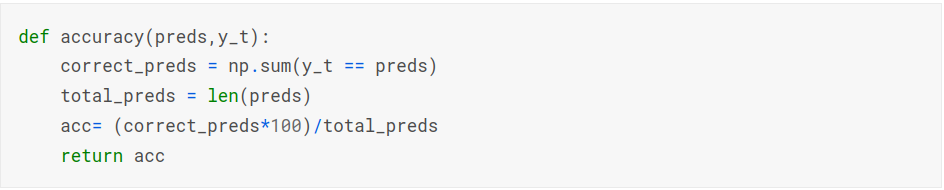
Accuracy Metric Implementation

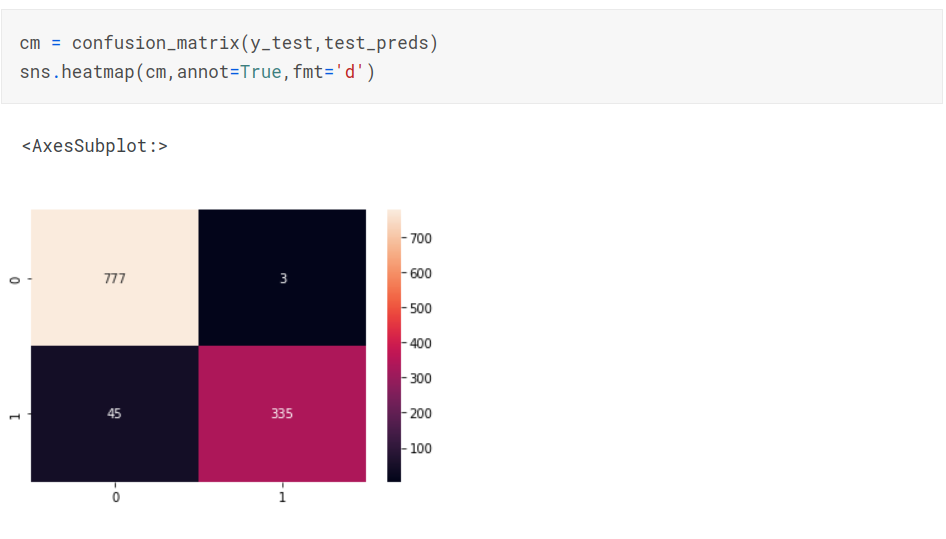
Confusion Matrix
Naive Bayes Model
Naive Bayes is one of the most popular models for spam classification. It is a probabilistic classifier that is based on Bayes theorem.
| 𝑃(𝑐 | 𝑥) = 𝑃(𝑥 | 𝑐) 𝑃(𝑐)/𝑃(𝑥) |
Here x stands for feature and c stands for class. Bernoulli Naive Bayes model is used for binary classification. The prediction is made on the basis of the equation:
| 𝑃(𝑥𝑖 | 𝑐) = 𝑃(𝑖 | 𝑐)𝑥𝑖 + (1 − 𝑃(𝑖 | 𝑐))(1 − 𝑥𝑖) |
The hyperparameter alpha can be used for smoothening. Hyperparameter tuning can be done using either grid search or randomized search. Naive Bayes model assumes that the features are independent of each other. It is fast and performs better with low amounts of training data.

Hyperparameter Tuning

Making predictions on test data
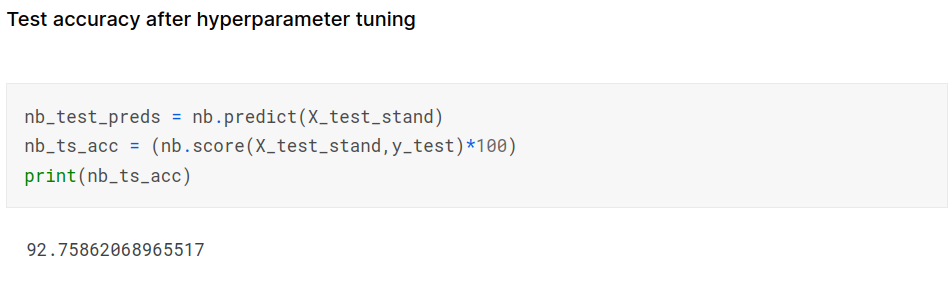
Confusion Matrix

Random Forest Classifier
Random Forest Model is an ensemble learning model that is constructed using multiple decision trees.Random forest also provides feature importance.

Making predictions on test data

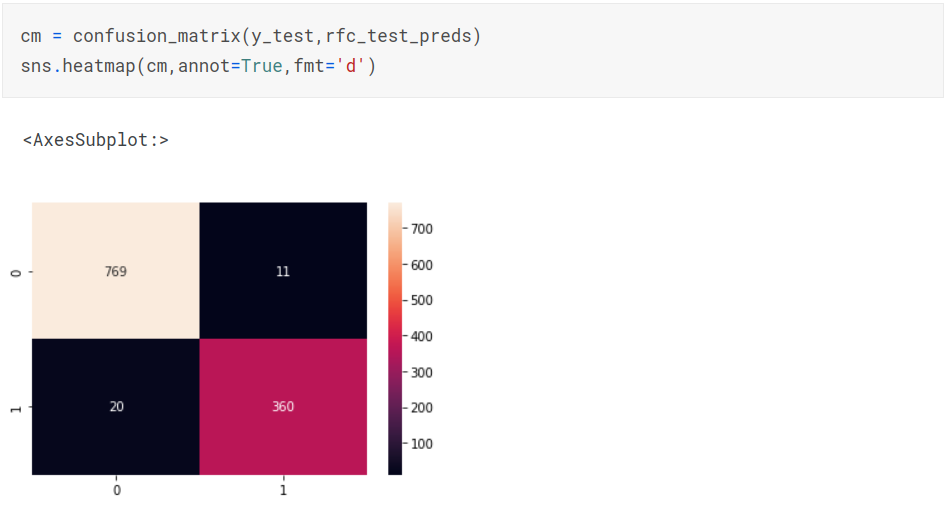
Confusion Matrix
Advanced Machine Learning Models
Stacking Classifier
A stacking model makes use of multiple learning models and combines their predictions and then uses another model on top of that to make the final predictions. This method improves the overall performance. The base models used in the project are a random forest classifier which is itself an ensemble model and Bernoulli Naive Bayes. The output from these models is then passed to the final estimator which in this case is logistic regression.

Making predictions on test data

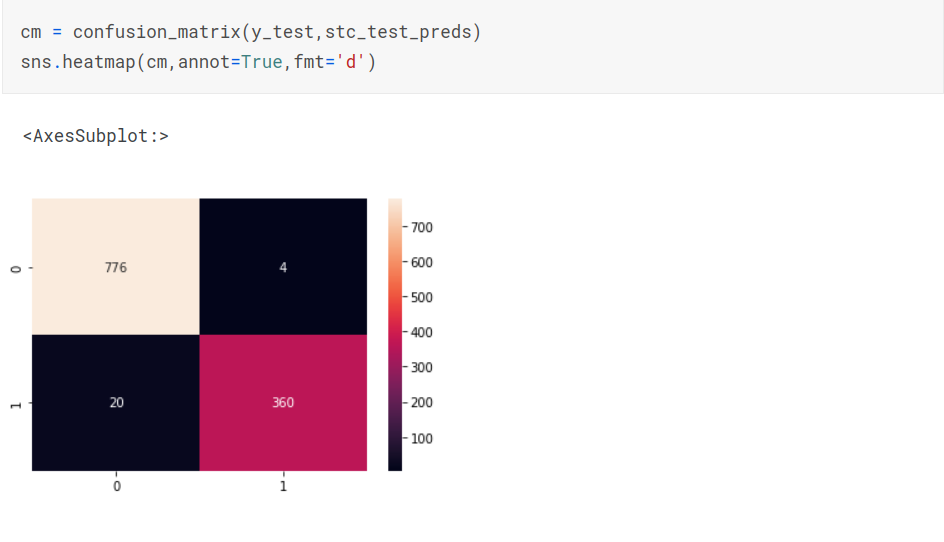
Confusion Matrix
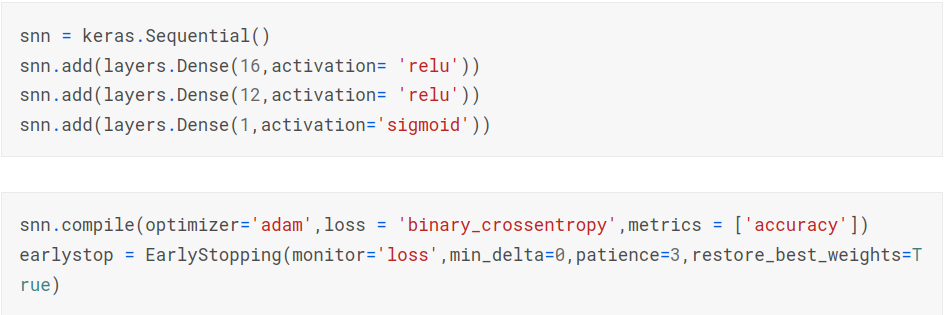
Neural Network Model
A neural network consists of a number of layers of nodes called neurons that are densely connected together. A weight value is assigned to each input received by a neuron. Each neuron has an activation function that it applies to the incoming connection. The activation function has to be non linear or there will be no difference between a neural network and a simple linear model. When a neural network is trained, weights and biases are initialized by different initialization methods. Then the input is passed through each layer and finally a loss value is computed by a loss function. Backpropagation is used to compute the derivative of loss function with respect to the weights of each input value using chain rule and memoization. An optimizer like gradient descent or stochastic gradient descent is used to update the weights and biases to get their optimal values. The state of the art optimizer used in most use cases is Adam. Neural networks provide a non linear decision boundary. Although neural networks are really powerful, for performing simple classification tasks, simple models are better suited as neural networks can easily overfit and lack interpretability
Making predictions on test data
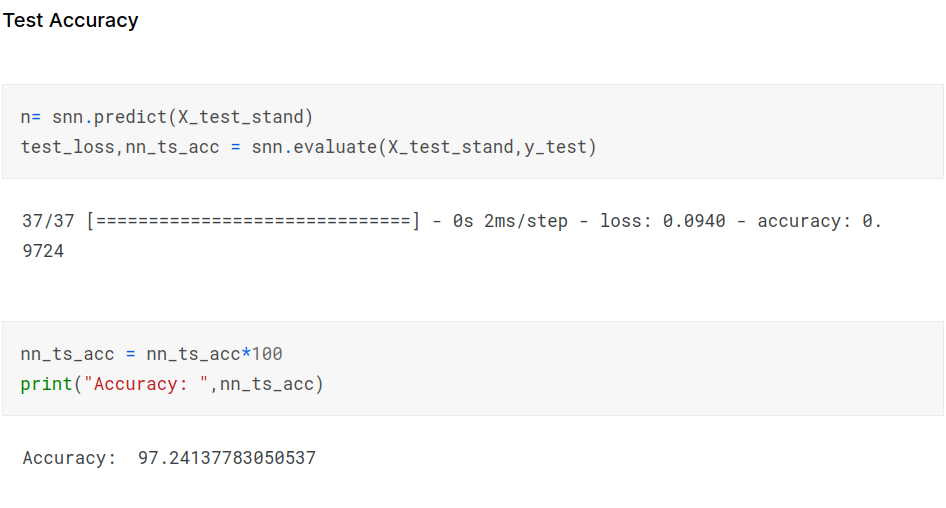
Confusion Matrix
Comparing all the models
Comparing train accuracy:
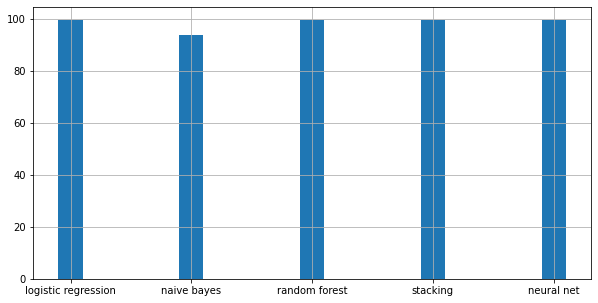
Comparing test accuracy:
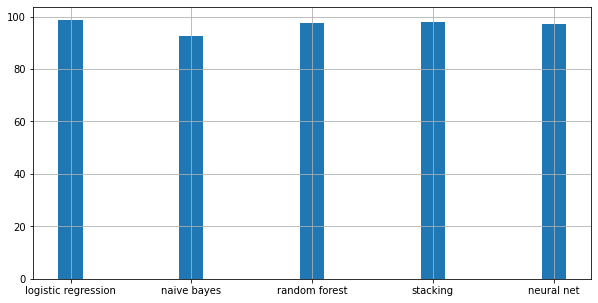
Conclusion:
Performance of a particular model depends on a lot of factors including the size of the dataset. In this case, a simple classification model like logistic regression gave the best performance.
References:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405844018353404